Trellis tree-based analysis reveals stromal regulation of patient-derived organoid drug responses
 Trellis Architecture
Trellis ArchitectureAbstract
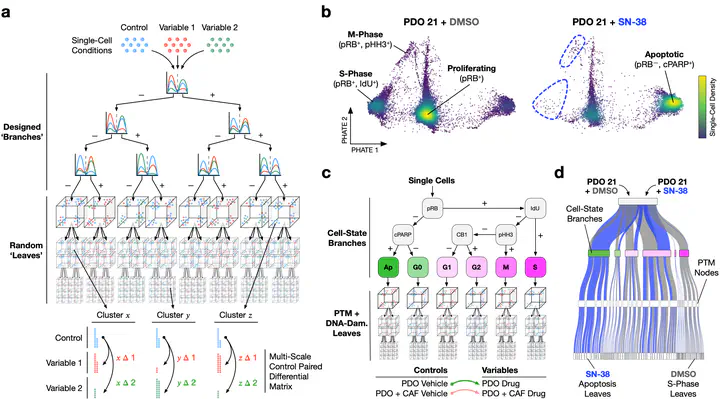
Patient-derived organoids (PDOs) can model personalized therapy responses; however, current screening technologies cannot reveal drug response mechanisms or how tumor microenvironment cells alter therapeutic performance. To address this, we developed a highly multiplexed mass cytometry platform to measure post-translational modification (PTM) signaling, DNA damage, cell-cycle activity, and apoptosis in >2,500 colorectal cancer (CRC) PDOs and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in response to clinical therapies at single-cell resolution. To compare patient- and microenvironment-specific drug responses in thousands of single-cell datasets, we developed “Trellis”—a highly scalable, tree-based treatment effect analysis method. Trellis single-cell screening revealed that on-target cell-cycle blockage and DNA-damage drug effects are common, even in chemorefractory PDOs. However, drug-induced apoptosis is rarer, patient-specific, and aligns with cancer cell PTM signaling. We find that CAFs can regulate PDO plasticity—shifting proliferative colonic stem cells (proCSCs) to slow-cycling revival colonic stem cells (revCSCs) to protect cancer cells from chemotherapy.